Core Competencies of University Students and Nursing Competencies: Literature Review
https://gexinonline.com/archive/journal-of-comprehensive-nursing-research-and-care/JCNRC-136
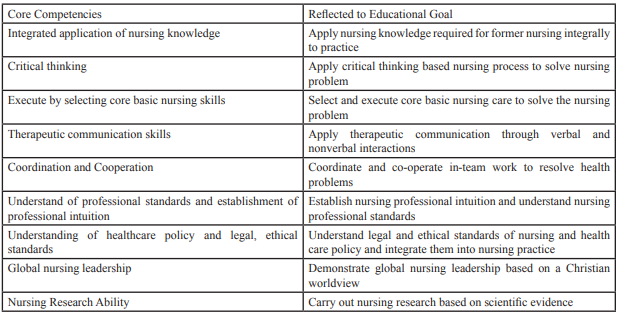
Review Result: K-CESA used in Korea as a core component of vocational competence refers to the knowledge, skills, and attitudes commonly required to perform a job successfully. Based on domestic and foreign literature, at a university of Korea has developed the BUCCA (Baekseok University Core Competency Assessment) consists of 6 areas, 17 outlines, and 69 items. Nursing students showed the higher level of servant leadership and spirit, calling, humanities than other major students. 7 nursing competencies are suggested by KABONE(Korea Accreditation board of Nursing Education) and a nursing curriculum developed based on that. A school of nursing in Korea develop 9 nursing competencies like as Integrated application of nursing knowledge, Critical thinking, Execute by selecting core basic nursing skills, Therapeutic communication skills, Coordination and Cooperation, Understand of professional standards and establishment of professional intuition, Understanding of healthcare policy and legal, ethical standards, Global nursing leadership, Nursing Research Ability.
Conclusion: A training course for nursing excellent nursing students should include both the core competencies needed by a college student and the nursing competencies to grow as a nurse. The two core competencies are closely related and this should be equally reflected in the curriculum and non subject programs. The development of innovative competency assessment methods is required in addition to the well-known CPE-based competency assessment.
The concept of core competency in the context of inter-firm competition in business administration is a factor explaining the superior ability, that is, the competitive advantage, over the competition. Since then, the core competencies were discussed as a conceptual basis for the direction of development of the curriculum of the university. The concept of core competency in college education is becoming generalized as a core connection concept of linkage between education and labor market that responds to corporate needs.
In college education, it is an important issue at this time to cultivate competence as a complex ability element for future through learnercentered learning activities rather than lectures based on the injection of existing knowledge [2]. It is necessary to constantly identify the core competencies that college students need to reflect on the timely demands.
In addition, nursing competency is the ability of general nurses to perform nursing work regardless of field [3]. It is a combination of knowledge, skills, and personal abilities to effectively perform professional work. The learning experience of nursing college curriculum affects the competency that is used in clinical practice after graduation. Therefore, the designing of educational curriculum centered on nursing competency is required and there is a need to continually explore the nursing capacity reflecting the changes of the times
In the main subject, the basic concepts of competency, core competencies of university students and nursing competency literature review will be provided, and the present status of Korea will be presented by reporting the development of core competency diagnostic tool for university students and nursing competency based curriculum development cases.
Until now the concept of competence has been designed and used mainly for companies, but after being linked with education, it was changed in the direction of acquiring theoretical and practical knowledge and to strengthen the actual work performance ability.
In college education, competency-based education with the concept of competency became important. It can be said that this is an education to evaluate students' achievement level based on the competence-related performance and by designing the curriculum through analysis of the actual role of modern society.
Therefore, competence as a cornerstone and guidance of educational planning, all elements of curriculum management such as selection and organization of education contents, teaching-learning methods and evaluation including setting of teaching-learning goals are progressed based on competency. Therefore, an efficient operation should be made by considering such facts [4].
For the competence centered curriculum, the achievement should be demonstrated after designing and operating the curriculum. Therefore, ongoing review of competencies can improve the quality of education and minimize fluctuations in educational outcomes [5].
The United States is pursuing college learning evaluation consisting of problem solving ability, analytical reasoning ability, critical thinking ability, and writing ability. Australia is conducting graduate skills assessment which includes communication/writing, problemsolving skills, interpersonal skills and teamwork, critical thinking skills, ethics and civic awareness, lifelong learning and information communication skills.
AHELO business of OECD has established and operates the higher education learning performance evaluation system complying with the International Academic Achievement Assessment (PISA). It includes general core competencies such as critical thinking, analytical reasoning, problem solving, and communication skills.It includes the field of major competence that measures knowledge and ability in the fields such as engineering and economics. It includes value-added measurement areas that measure the effects of college on learning outcomes, and a background factor area including information on country/school/student.
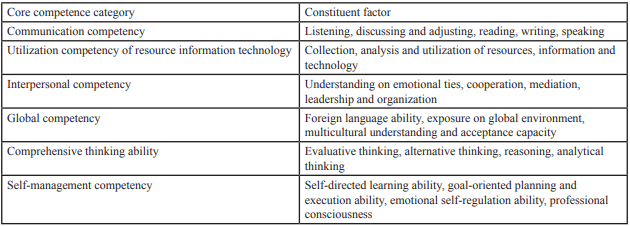
The Korea Collegiate Essential Skills Assessment (K-CESA) used in Korea as a core component of vocational competence refers to the knowledge, skills, and attitudes commonly required to perform a job successfully. K-CESA consists of 6 core competencies such as communication competency, global competency, utilization competency of resource information technology, comprehensive thinking ability, interpersonal capacity and self-management competency (Table-1). It is used to diagnose core competency level of college students [1,7]. Based on domestic and foreign literature, at a university of Korea has developed the Baekseok University Core Competency Assessment (BU-CCA) and been using it since 2016 [8].
When looking at the research related to university students' core competency, in the study of [6] analyzing the core competence and relevance of academic achievement showed that there is an increase in the achievement of core competencies as the grade increases [9]. However, it was reported that global competency score was low. It claimed that although international exchanges have increased, understanding and acceptance capacity of multicultural situations did not improve relatively.
In the study by [10], in the major subject, the need for science education was high at 2.91 [10]. Especially, it was reported that need for education was shown in the order of career development ability, information processing ability, interpersonal ability, communication ability, and problem solving ability. Especially, the Department of Engineering and Social Sciences had higher demand for creativity. Most students had high educational needs for all core competencies, and suggested that institutional coordination is required so that students can apply the class division by departments. Lee et al. [6] reported that analytical thinking, problem solving, and critical thinking of university students were related to academic achievements but claimed that creative thinking was not related to academic achievement [9].
When gathering the results of various studies, core competencies of university students were related to academic achievements as the grade increased, so there is a need to sufficiently reflect such results when designing a major curriculum.In addition, creative curriculum activities such as developing educational policies to enhance global competence for Korean university students and incorporating creative activities into the curriculum should be emphasized.
Kim, [11] has analyzed the differences in core competencies among nursing students and other major students [11]. Nursing students showed the higher level of servant leadership and spirit, calling, humanities than others. Main factors to affect major satisfaction field practice. To raise up the good point, it is need to consider strategies how to strengthen them in curriculum (Table-2).
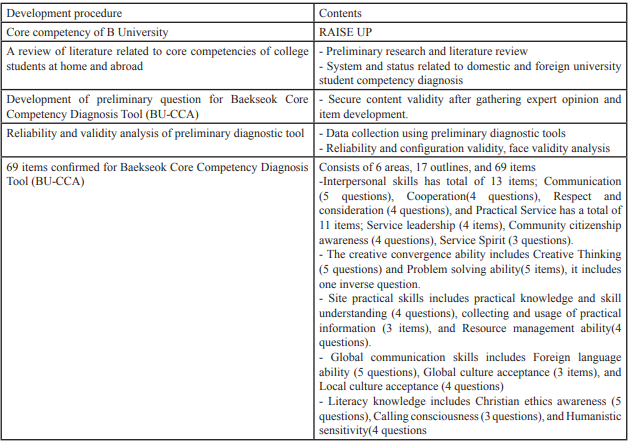
Table 2: Development case of core competency diagnostic tools for a Korean university: BU-CCA development procedure and contents.
In Korea, based on domestic and foreign research results since 2012, has identified the core competencies of nurses commonly required for performing various duties at clinical sites 2-3 years after the graduation and there is movement to operate the curriculum reflecting this.
In Korea, according to the Medical Law, all nursing departments are required to receive accreditation and this is administered by the Korea Nursing Education and Research Institute. Table 4 is the core competency of nurses and its definition presented by the Korea Nursing Education Evaluation Institute [14].
At a university in Korea, a competency-based curriculum was operated by identifying and reflecting the core competencies of nursing students into educational goals. A questionnaire was conducted on the core competencies of nurses targeting graduates and clinical nursing managers and a comprehensive analysis was made by reflecting the job analysis results and health care policy. The core competencies for nursing student education are shown in Table 5.
When examining the study on the nursing competency and core competence targeting nursing students, a recent increase can be seen. Bac [15] has studied the structural equation modeling on core competencies of nursing students, where the satisfaction with major and clinical practice has an indirect effect on nursing core competencies, and the critical thinking tendency was reported to have shown a direct effect [15]. Therefore, to promote nursing core competencies, a satisfaction of major should be promoted through curriculum process development, comparison of core competencies and strengthening of education that improve critical thinking, and it is necessary to develop strategies for clinical practice education and practice guidance.
Kim [16] has conducted a descriptive study in order to investigate whether the learning experience of nursing college students affected the enhancement of core competencies using K-NSSE valuated by Bae [16-17]. Among the core competencies of the survey subjects, interpersonal skills were 3.96, creative convergence competencies were 3.95, site practical skills were 3.68, and global communication competencies were 3.49 showing that figures were above the middle. Among the learning experience factor, 'academic challenge' and 'learning with peers' were related to all core competencies and reported that academic challenge was the highest [16]. Therefore, to improve the core competency level of nursing college students, teaching methods that strengthens reflective integrated learning, higher-level learning, and learning strategies are needed by applying it into the curriculum process.New teaching and learning strategies that can inspire critical thinking by avoiding existing simple memorization-oriented nursing education should be developed and applied. There is also a need to continue to explore the curriculum and out-of-curriculum that can be done with colleagues.
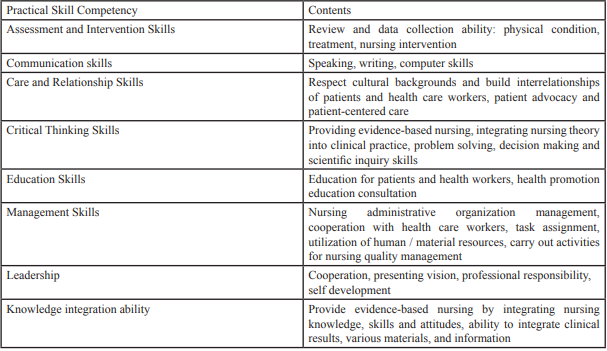
Lerburg et al. [13] suggest that nursing students should raise their 8 competencies including communication skill, human relationships, management and knowledge integration in COPA model [13]. These competencies are very related with nursing field after school. So Strategies need to be developed in CPE in the simulation or other methods.
Journal of Comprehensive Nursing Research and Care Volume 3 (2018), Article ID: JCNRC-136
https://doi.org/10.33790/jcnrc1100136Research Article
Core Competencies of University Students and Nursing Competencies: Literature Review
Jihyun Kim
Teaching lecture of nursing management, Department of Nursing, Baekseok University, South Korea.
Corresponding Author Details:
Jihyun Kim, Department of Nursing, Teaching lecture of nursing management, Baekseok University,
Chohyunggwan Office No. 724, 76 Moonamro, South Korea.
E-mail: jhkimrn@bu.ac.k
Received date: 21st November, 2018
Accepted date: 31st January, 2019
Published date: 05th March, 2019
Accepted date: 31st January, 2019
Published date: 05th March, 2019
Citation: Kim J (2019) Core Competencies of University Students and Nursing Competencies : Literature Review. J Comp
Nurs Res Care 4: 136.
Copyright: ©2019, This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author
and source are credited
Abstract
Background: core competency has begun to be emphasized as a key element for the university students preparing for the future as well as for the learning ability of leaner. Competence refers to the basic knowledge needed by the students and ability, power, skill, function, manner and attitude related to problem solving. Nursing competency is the ability of general nurses to perform nursing work regardless of field. It is a combination of knowledge, skills, and personal abilities to effectively perform professional work. The purpose of this research is that the basic concepts of competency, core competencies of university students and nursing competency literature review will be provided, and discuss the present status of Korea presented by reporting.Review Result: K-CESA used in Korea as a core component of vocational competence refers to the knowledge, skills, and attitudes commonly required to perform a job successfully. Based on domestic and foreign literature, at a university of Korea has developed the BUCCA (Baekseok University Core Competency Assessment) consists of 6 areas, 17 outlines, and 69 items. Nursing students showed the higher level of servant leadership and spirit, calling, humanities than other major students. 7 nursing competencies are suggested by KABONE(Korea Accreditation board of Nursing Education) and a nursing curriculum developed based on that. A school of nursing in Korea develop 9 nursing competencies like as Integrated application of nursing knowledge, Critical thinking, Execute by selecting core basic nursing skills, Therapeutic communication skills, Coordination and Cooperation, Understand of professional standards and establishment of professional intuition, Understanding of healthcare policy and legal, ethical standards, Global nursing leadership, Nursing Research Ability.
Conclusion: A training course for nursing excellent nursing students should include both the core competencies needed by a college student and the nursing competencies to grow as a nurse. The two core competencies are closely related and this should be equally reflected in the curriculum and non subject programs. The development of innovative competency assessment methods is required in addition to the well-known CPE-based competency assessment.
Introduction
Recently, the term competency or core competency has begun to be emphasized as a key element for the university students preparing for the future as well as for the learning ability of leaner. Competence refers to the basic knowledge needed by the students and ability, power, skill, function, manner and attitude related to problem solving [1].The concept of core competency in the context of inter-firm competition in business administration is a factor explaining the superior ability, that is, the competitive advantage, over the competition. Since then, the core competencies were discussed as a conceptual basis for the direction of development of the curriculum of the university. The concept of core competency in college education is becoming generalized as a core connection concept of linkage between education and labor market that responds to corporate needs.
In college education, it is an important issue at this time to cultivate competence as a complex ability element for future through learnercentered learning activities rather than lectures based on the injection of existing knowledge [2]. It is necessary to constantly identify the core competencies that college students need to reflect on the timely demands.
In addition, nursing competency is the ability of general nurses to perform nursing work regardless of field [3]. It is a combination of knowledge, skills, and personal abilities to effectively perform professional work. The learning experience of nursing college curriculum affects the competency that is used in clinical practice after graduation. Therefore, the designing of educational curriculum centered on nursing competency is required and there is a need to continually explore the nursing capacity reflecting the changes of the times
In the main subject, the basic concepts of competency, core competencies of university students and nursing competency literature review will be provided, and the present status of Korea will be presented by reporting the development of core competency diagnostic tool for university students and nursing competency based curriculum development cases.
Main Subject
Competency
Competency is 1) precise and measurable action execution, 2) ability to use appropriate knowledge and skills in specific situations, 3) sufficient degree of ability and standard, 4) General qualities or conditions that characterize a person. Ultimately, competence can be seen as the ability that a student must have at the time of graduation.Until now the concept of competence has been designed and used mainly for companies, but after being linked with education, it was changed in the direction of acquiring theoretical and practical knowledge and to strengthen the actual work performance ability.
In college education, competency-based education with the concept of competency became important. It can be said that this is an education to evaluate students' achievement level based on the competence-related performance and by designing the curriculum through analysis of the actual role of modern society.
Therefore, competence as a cornerstone and guidance of educational planning, all elements of curriculum management such as selection and organization of education contents, teaching-learning methods and evaluation including setting of teaching-learning goals are progressed based on competency. Therefore, an efficient operation should be made by considering such facts [4].
For the competence centered curriculum, the achievement should be demonstrated after designing and operating the curriculum. Therefore, ongoing review of competencies can improve the quality of education and minimize fluctuations in educational outcomes [5].
Core Competencies of University students
Core competencies, in terms of employment and labor market, becomes the evaluation criteria to replace qualifications such as degrees and credits, and in terms of education and training institutions, it has the meaning as a criterion that defines the goals and contents of the curriculum [6].The United States is pursuing college learning evaluation consisting of problem solving ability, analytical reasoning ability, critical thinking ability, and writing ability. Australia is conducting graduate skills assessment which includes communication/writing, problemsolving skills, interpersonal skills and teamwork, critical thinking skills, ethics and civic awareness, lifelong learning and information communication skills.
AHELO business of OECD has established and operates the higher education learning performance evaluation system complying with the International Academic Achievement Assessment (PISA). It includes general core competencies such as critical thinking, analytical reasoning, problem solving, and communication skills.It includes the field of major competence that measures knowledge and ability in the fields such as engineering and economics. It includes value-added measurement areas that measure the effects of college on learning outcomes, and a background factor area including information on country/school/student.
The Korea Collegiate Essential Skills Assessment (K-CESA) used in Korea as a core component of vocational competence refers to the knowledge, skills, and attitudes commonly required to perform a job successfully. K-CESA consists of 6 core competencies such as communication competency, global competency, utilization competency of resource information technology, comprehensive thinking ability, interpersonal capacity and self-management competency (Table-1). It is used to diagnose core competency level of college students [1,7]. Based on domestic and foreign literature, at a university of Korea has developed the Baekseok University Core Competency Assessment (BU-CCA) and been using it since 2016 [8].
When looking at the research related to university students' core competency, in the study of [6] analyzing the core competence and relevance of academic achievement showed that there is an increase in the achievement of core competencies as the grade increases [9]. However, it was reported that global competency score was low. It claimed that although international exchanges have increased, understanding and acceptance capacity of multicultural situations did not improve relatively.
In the study by [10], in the major subject, the need for science education was high at 2.91 [10]. Especially, it was reported that need for education was shown in the order of career development ability, information processing ability, interpersonal ability, communication ability, and problem solving ability. Especially, the Department of Engineering and Social Sciences had higher demand for creativity. Most students had high educational needs for all core competencies, and suggested that institutional coordination is required so that students can apply the class division by departments. Lee et al. [6] reported that analytical thinking, problem solving, and critical thinking of university students were related to academic achievements but claimed that creative thinking was not related to academic achievement [9].
When gathering the results of various studies, core competencies of university students were related to academic achievements as the grade increased, so there is a need to sufficiently reflect such results when designing a major curriculum.In addition, creative curriculum activities such as developing educational policies to enhance global competence for Korean university students and incorporating creative activities into the curriculum should be emphasized.
Kim, [11] has analyzed the differences in core competencies among nursing students and other major students [11]. Nursing students showed the higher level of servant leadership and spirit, calling, humanities than others. Main factors to affect major satisfaction field practice. To raise up the good point, it is need to consider strategies how to strengthen them in curriculum (Table-2).

Table 2: Development case of core competency diagnostic tools for a Korean university: BU-CCA development procedure and contents.
Nursing Competency
Nursing competency is the ability of general nurses to perform nursing work regardless of field. Nursing core competencies is an important capability that is essential to carry out their duties and proving the professionality of the nurse [3]. Lenburg [12] has presented 8 kinds of nursing competencies and specific practical skills in his COPA model (Competency Outcome Practice Assessment Model) [12-13] (Table-3).In Korea, based on domestic and foreign research results since 2012, has identified the core competencies of nurses commonly required for performing various duties at clinical sites 2-3 years after the graduation and there is movement to operate the curriculum reflecting this.
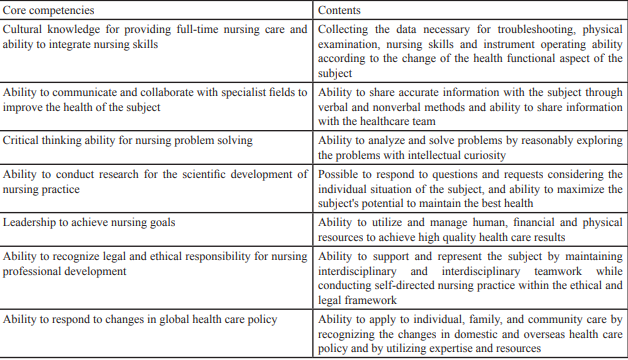
In Korea, according to the Medical Law, all nursing departments are required to receive accreditation and this is administered by the Korea Nursing Education and Research Institute. Table 4 is the core competency of nurses and its definition presented by the Korea Nursing Education Evaluation Institute [14].
At a university in Korea, a competency-based curriculum was operated by identifying and reflecting the core competencies of nursing students into educational goals. A questionnaire was conducted on the core competencies of nurses targeting graduates and clinical nursing managers and a comprehensive analysis was made by reflecting the job analysis results and health care policy. The core competencies for nursing student education are shown in Table 5.
When examining the study on the nursing competency and core competence targeting nursing students, a recent increase can be seen. Bac [15] has studied the structural equation modeling on core competencies of nursing students, where the satisfaction with major and clinical practice has an indirect effect on nursing core competencies, and the critical thinking tendency was reported to have shown a direct effect [15]. Therefore, to promote nursing core competencies, a satisfaction of major should be promoted through curriculum process development, comparison of core competencies and strengthening of education that improve critical thinking, and it is necessary to develop strategies for clinical practice education and practice guidance.
Kim [16] has conducted a descriptive study in order to investigate whether the learning experience of nursing college students affected the enhancement of core competencies using K-NSSE valuated by Bae [16-17]. Among the core competencies of the survey subjects, interpersonal skills were 3.96, creative convergence competencies were 3.95, site practical skills were 3.68, and global communication competencies were 3.49 showing that figures were above the middle. Among the learning experience factor, 'academic challenge' and 'learning with peers' were related to all core competencies and reported that academic challenge was the highest [16]. Therefore, to improve the core competency level of nursing college students, teaching methods that strengthens reflective integrated learning, higher-level learning, and learning strategies are needed by applying it into the curriculum process.New teaching and learning strategies that can inspire critical thinking by avoiding existing simple memorization-oriented nursing education should be developed and applied. There is also a need to continue to explore the curriculum and out-of-curriculum that can be done with colleagues.
Lerburg et al. [13] suggest that nursing students should raise their 8 competencies including communication skill, human relationships, management and knowledge integration in COPA model [13]. These competencies are very related with nursing field after school. So Strategies need to be developed in CPE in the simulation or other methods.
Conclusion
A training course for nursing excellent nursing students should include both the core competencies needed by a college student and the nursing competencies to grow as a nurse. The two core competencies are closely related and this should be equally reflected in the curriculum and co-curriculum programs. And periodically, it should be used to improve the curriculum by exploring the needs of students and clinical sites and by evaluating the achievement of competencies. In order to do so, the development of innovative competency assessment methods is required in addition to the wellknown CPE-based competency assessment.Conflict of interest
The author has no conflict of interest.Acknowledgement
This artice was supported by a grant from Baekseok University.References
- Jin MS (2013) 2012 K-CESA diagnosis support project KRIVET
(Korea Research Institute for Vocational Education & Training).View
- Caligiuri P, Santo DV (2001) Global competence: what is it, and
can it be developed through global assignments? Human Res
Plan 3: 27-35.
-
International Council of Nurses (2008) Nursing Care Continuum
Framework and Competencies, ICN Regulation Series.View
- Park Young, Kim A, Ja-Kyung K, Chung MS, Bang KS et al.
(2013) An Identification Study on Core Nursing Competency. J
Korean Acad Soc Nurs Edu 4: 663-674.
- Model TF, Bird JL (2010) Continuous curriculum review in a
bachelor of nursing program: preventing curriculum drift and
improving quality. J Nurs Edu 10: 592-595.
View
- Lee JIK, Kim JH (2012) A study on the relationship between
college students' essential skills and academic achievement. J
Vocat Edu Res 31: 227-246.
- Park IS, Jeon HN (2015) The effect of core competency on
stress coping and problem solving ability of nursing students.
Proceeding of the 4th K-CESA conference.
- Kim J, Gum HJ, Lim MR, Yim SY, Shin SH, et al. (2017)
Development of BU-CCA,(Baekseok Core Competency
Assessment tool). Baekseok University Press.
- Kim HY, Lee SJ (2012) Diagnosis and direction of the
competence-based educational model: Based on the courses and
Effects. J Gen Edu 4: 11-40.
- Heojeong Y, Bang D (2015) Analysis of undergraduate students'
educational needs for key competencies in curriculum of major
subject and liberal arts. J Learner-Centered Curric Instr 15: 567-
584.
- Jihyun Kim (2017) Difference in Core Competence and
Major Satisfaction Factors among Nursing Students and Other
Undergraduates. Proceeding of 2017 International conference
on convergence technology.
- Lenburg C, Klein C, Abdur-Rahman V, Spencer T, Boyer S, et
al. (2009) A Comprehensive Framework Designed to Promote
Quality Care and Competence for Patient Safety. Nursing
Education Perspectives 5: 312-317.View
- Lenburg C, Abdur-Rahman V, Spencer T, Boyer S, Klein C et
al. (2011) Implementing the COPA model in nursing education
and practice settings: promoting competence, quality care, and
patient safety. Nurs Edu Perspect 5: 290-296.
View
- Korea Accreditation board of Nursing Education (2012)
Teaching workshop for performance-based curriculum
management.
- Bae DY (2016) Structural equation modeling on core
competencies of nursing students on graduation time. Doctoral
dissertation of Kyoungsang University, Korea.
- . Kim J (2018) Effects of Learning Experience on Core
Competencies of Nursing Students.
- Bae SH, Kang MS, Hong JI (2015) Validation of the National
Survey of Student Engagement (NSSE) Model in the Korean
Context. Asian J Edu 4: 77-104.
Core Competencies of University Students and Nursing Competencies: Literature Review ,
Literature Review Core Competencies of University Students and Nursing Competencies ,
Core Competencies University Students and Nursing Competencies Literature Review ,
University Students and Nursing Competencies Literature Review Core Competencies ,
Core Competencies Nursing Competencies University Students Literature Review ,
Nursing Competencies Literature Review Core Competencies ,
Literature Review Core Competencies of University Students ,
Core Competencies of University Students Literature Review ,
The topic "Core Competencies of University Students and Nursing Competencies: Literature Review" is crucial for understanding how academic and practical skills intersect in healthcare education. For students struggling to analyze and synthesize such comprehensive literature, seeking professional guidance can be beneficial. Resources like university assignment help provide structured support, ensuring clarity in research, proper referencing, and in-depth insights. Leveraging such assistance can significantly improve the quality of academic submissions while enhancing understanding of essential nursing competencies.
ReplyDelete